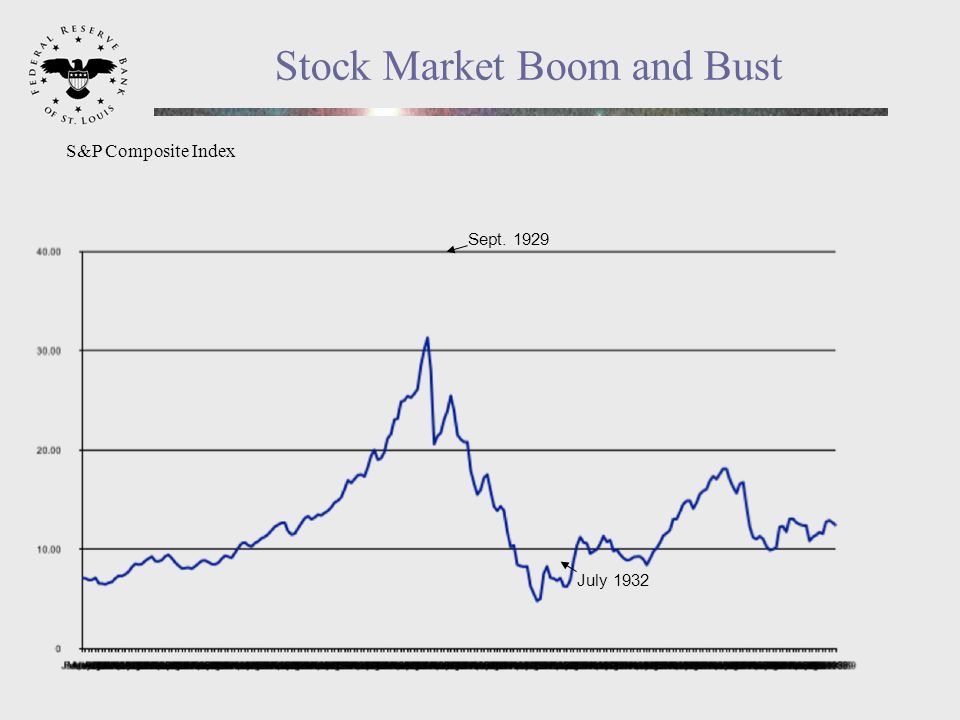
Boom bust stock market
In the boom cycle, growth is positive. It accompanies a bull market , rising housing prices, wage growth and low unemployment. That's when there's too much liquidity in the money supply , leading to inflation.
You know you're at the end of a boom phase when the media says the expansion will never end, and even the grocery clerk is making money from the latest asset bubble. The bust phase is like life in the Middle Ages--brutish, nasty, and mercifully short. It usually only lasts 18 months or less. If it lasts more than three months, it's usually a recession.
For more, see How a Stock Market Crash Can Cause a Recession. Three forces combine to create the cycle of boom and bust. Strong consumer demand drives the boom phase.
Families are confident about the future, so they buy more now, knowing they'll get better jobs, higher home values, and rising stock prices later on.
This demand means companies have boost supply, which they do by hiring new workers. Capital is easily available, so consumers and businesses alike can borrow at low rates. They ignore the risk to achieve gain. Plummeting confidence causes the bust cycle. Investors and consumers get nervous when the stock market corrects or even a crashes.
As companies lay off workers, consumers lose their jobs and stop buying anything but necessities. That causes a downward spiral. The bust cycle eventually stops on its on. That happens when prices are so low that those investors that still have cash start buying again.
However, this can take a long time, and even lead to a depression. It uses economic indicators to measure the boom and bust cycles. Since , there have been 33 cycles. On average, the booms last For more, see NBER Cycles. Search the site GO. US Economy GDP and Growth Recessions Economic Sectors Natural Disasters GDP by Year Economic Theory Supply Demand National Debt Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy Trade Policy Inflation U. Markets World Economy Economy Stats Hot Topics Glossary.
Updated December 28, Bust May - Jun FDR tried to balance budget. Boom Jul - Jan World War II mobilization. Boom Nov - Oct Employment Act. Bust Nov - Oct Postwar adjustment Boom Nov - Jun Korean War mobilization. Bust Jul - May Peacetime demoblization.
Boom Jun - Jul Fed reduced rate to 1. Bust Aug - Apr Fed raised rate to 3. Boom May - Mar Fed lowered rate to 0.
Merck Stock History: The Drugmaker's Boom, Bust, and Bounce Back -- The Motley Fool
Bust Apr - Feb Fed raised rate to 4. Boom Mar - Nov JFK stimulus spending.
Fed lowered rate to 1. Bust Dec - Nov Fed raised rate to 9.
Dot-com bubble - Wikipedia
Boom Dec - Oct Fed lowered rate to 3. Bust Nov - Mar Nixon added wage-price controls. Boom Apr - Dec Fed lowered rate to 4. Boom Aug - Jun Fed lowered rates. For more, see Historical Fed Funds Rates.
Bust Jul - Nov Resumption of recession. Get Daily Money Tips to Your Inbox Email Address Sign Up. There was an error. Please enter a valid email address. Personal Finance Money Hacks Your Career Small Business Investing About Us Advertise Terms of Use Privacy Policy Careers Contact. Nixon added wage-price controls. Derivatives created housing bubble in Subprime Mortgage Crisis , Financial Crisis , the Great Recession.